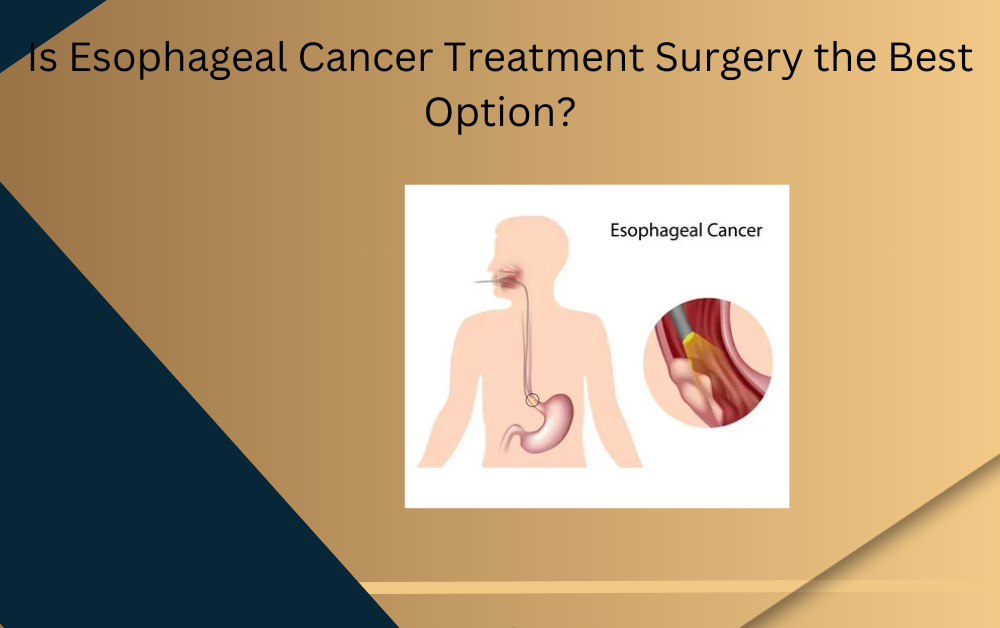
Esophageal cancer is a life-threatening condition that affects the esophagus, the muscular tube connecting the throat to the stomach.
While multiple treatment options are available, surgery remains one of the most effective solutions, especially for cases where cancer has not widely metastasized. But is surgery always the best choice? Understanding its procedures, risks, and post-surgical care is crucial for making informed decisions.
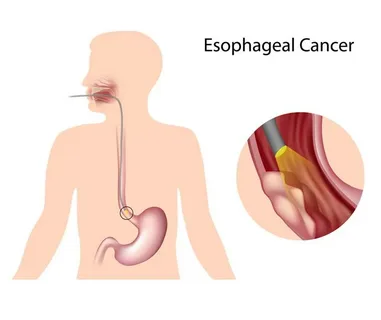
Note: Esophageal cancer treatment surgery has been a crucial step in managing the disease, offering patients a chance at extended survival and improved quality of life. At DrDameh, expert oncologists have successfully performed numerous procedures, ensuring comprehensive cancer care. If you or a loved one is seeking expert guidance, contact DrDameh today.
Table of Contents
Understanding Esophageal Cancer Treatment Surgery
Surgical treatment for esophageal cancer involves removing the affected portion of the esophagus to prevent further spread. The procedure is often combined with chemotherapy and radiation therapy to enhance outcomes. The choice of surgery depends on factors like cancer stage, location, and the patient’s overall health.
Types of Esophageal Cancer Surgery
1. Esophagectomy
Esophagectomy is the most common surgical procedure for esophageal cancer. It involves the removal of part or the entire esophagus, followed by reconstructing the digestive tract using a portion of the stomach or colon.
2. Endoscopic Resection
This is a minimally invasive surgery used for early-stage esophageal cancer. It involves removing small cancerous growths through an endoscope without making external incisions.
3. Palliative Surgery
For patients in advanced stages, surgery may not be curative but can help relieve symptoms. This includes procedures like esophageal stent placement or gastric bypass to improve swallowing and nutrition intake.
How Esophageal Cancer Surgery is Performed
Pre-Surgical Preparations
Before surgery, patients undergo various tests such as imaging scans, endoscopy, and biopsies to assess cancer spread. Doctors may recommend dietary adjustments and cessation of smoking or alcohol consumption.
Surgical Procedure
- Traditional Surgery: A large incision is made in the chest or abdomen to remove the cancerous part of the esophagus.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Laparoscopic or robotic-assisted surgery is performed using small incisions, reducing recovery time.
- Reconstruction: The stomach or intestine is reshaped and connected to the remaining esophagus for digestion continuity.
Post-Surgical Care
After surgery, patients may require temporary feeding tubes, followed by a gradual return to normal eating. Regular follow-ups ensure proper healing and monitor potential complications.
Risks and Complications of Esophageal Cancer Surgery
1. Infection and Bleeding
As with any major surgery, there is a risk of infections and internal bleeding, which requires close monitoring.
2. Leakage from the Surgical Connection
One of the primary concerns is leakage at the site where the esophagus is reattached to the stomach. This may need further corrective surgery.
3. Swallowing Difficulties
Patients may experience dysphagia (difficulty swallowing) post-surgery, which can be managed with dietary modifications or therapy.
4. Long-Term Digestive Issues
Many patients experience acid reflux, delayed stomach emptying, or unintentional weight loss after esophageal cancer treatment surgery.
Recovery After Esophageal Cancer Surgery
Hospital Stay and Initial Recovery
Patients usually stay in the hospital for 1-2 weeks, during which vital signs are monitored, and tube feeding is provided. Pain management is crucial during this period.
Nutritional Adjustments
A liquid or soft diet is recommended initially. Over time, small, frequent meals help ease digestion.
Physical Rehabilitation
Walking and light physical activity are encouraged to prevent blood clots and improve overall recovery.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Post-surgery, many patients face emotional challenges such as anxiety and depression. Counseling and support groups can aid in coping with the changes.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
While surgery is the primary treatment, some patients explore additional therapies such as:
- Nutritional Therapy: Special diets to aid digestion.
- Acupuncture: Helps manage post-surgical pain.
- Yoga & Meditation: Improves overall well-being and reduces stress.
When to Seek Medical Help Post-Surgery
Patients should consult their doctor if they experience:
- Severe chest or abdominal pain
- Persistent nausea or vomiting
- Difficulty swallowing
- Fever or signs of infection
- Unintended rapid weight loss
Conclusion
Esophageal cancer treatment surgery remains a vital option for managing and potentially curing esophageal cancer. While it carries certain risks, advancements in medical techniques have significantly improved patient outcomes. If you or a loved one is considering surgical treatment, consult a trusted medical professional for personalized guidance.
For More Insightful Articles Related To This Topic, Feel Free To Visit: motherboardguid